Ultrafast Molecular Stitching of Graphene Films at the Ethanol/Water Interface for High Volumetric Capacitance
Gang Lian,* Chia-Chi Tuan, Liyi Li, Shilong Jiao, Kyoung-Sik Moon, Qilong Wang, Deliang Cui, and Ching-Ping Wong*
Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1365-1370
Abstract
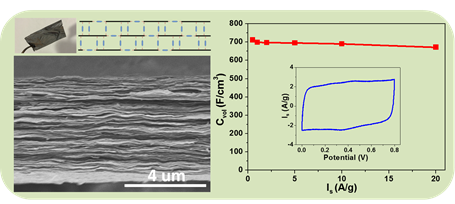
Compact graphene film electrodes with a high ion accessible surface area have the promising potential to realize high density electrochemical energy storage (or high volumetric capacitance), which is vital for the development of flexible, portable, and wearable energy storage devices. Here, a novel, ultrafast strategy for stitching graphene sheets into films, in which p-phenylenediamine (PPD) molecules are uniformly intercalated between the graphene sheets, is simply constructed at the ethanol/water interface. Due to uniformly interlayer spacing (∼1.1 nm), good wettability, and an interconnected ion transport channel, the binder-free PPD-graphene film with a high packing density (1.55 g cm-3) delivers an ultrahigh volumetric capacitance (711 F cm-3 at a current density of 0.5 A g-1), high rate performance, high power and energy densities, and excellent cycling stability in aqueous electrolytes. This interfacial stitching strategy holds new promise for the future design of enhanced electrochemical energy storage devices.